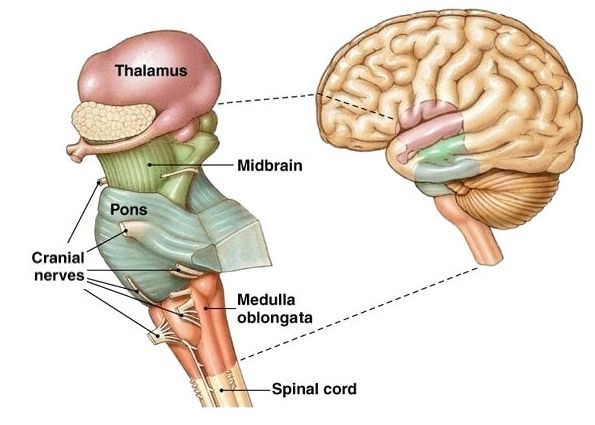
The Brain Stem.
The brain stem is comprised of the midbrain, pons, and medulla:
The Midbrain – The midbrain is often considered the smallest region of the brain. It acts as a sort of relay station for auditory and visual information. The midbrain controls many important functions such as the visual and auditory systems as well as eye movement. Portions of the midbrain called the red nucleus and the substantia nigra are involved in the control of body movement. The darkly pigmented substantia nigra contains a large number of dopamine-producing neurons are located. The degeneration of neurons in the substantia nigra is associated with Parkinson’s disease.
The Medulla – The medulla is located directly above the spinal cord in the lower part of the brain stem and controls many vital autonomic functions such as heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure.
The Pons – The pons connects the cerebral cortex to the medulla and to the cerebellum and serves a number of important functions including playing a role in several autonomic functions such as stimulating breathing and controlling sleep cycles.